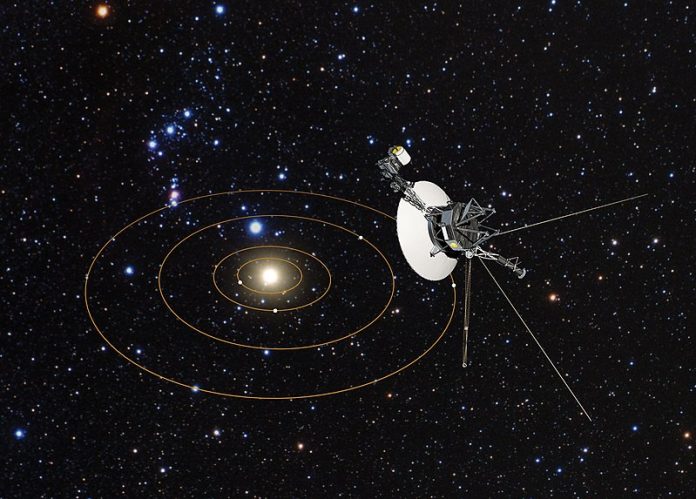
Voyager 1, the most distant man-made object in history, has resumed sending signal to the Earth after a gap of five months. On 14 November 2023, It had stopped sending readable science and engineering data to Earth following a glitch in onboard computers even though it was receiving commands from mission control and otherwise operated normally.
The three onboard computers, called the flight data subsystem (FDS) which packages the science and engineering data before it’s sent to Earth had malfunctioned because a single chip and some software codes were not working. This made science and engineering data unusable. An innovative approach to address the issue was successful and the mission team heard back from Voyager 1 on 20 April 2024 and were able to check the health and status of the spacecraft after a gap of five months.
The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again.
Currently, Voyager 1 is over 24 billion kilometres away from Earth. A radio signal takes about 22 ½ hours to reach Voyager 1 and another 22 ½ hours to return to Earth.
The twin Voyager spacecrafts are the longest-running and most distant spacecraft in history.
Voyager 2 was launched first, on 20th August 1977; Voyager 1 was launched on a faster, shorter trajectory on 5th September 1977. Since their launches, Voyager 1 and 2 spacecrafts are continuing on their over-46-year journey and are now exploring interstellar space where nothing from Earth has flown before.
It was Voyager 1 that took the famous Pale Blue Dot photograph of Earth on 14 February 1990, from a record distance of about 6 billion kilometres before leaving the solar system.
On 25th August 2012, Voyager 1 made history when it entered into interstellar space. It was the first spacecraft to cross the heliosphere. It is the first human-made object to venture into interstellar space.
Before entering interstellar space, Voyager 1 made significant contributions to our knowledge of solar system. It discovered a thin ring around Jupiter and two new Jovian moons: Thebe and Metis. At Saturn, Voyager 1 found five new moons and a new ring called the G-ring.
Voyager Interstellar Mission (VIM) is exploring the outermost edge of the Sun’s domain. And beyond.
***
Sources:
- NASA’s Voyager 1 Resumes Sending Engineering Updates to Earth. Posted 22 April 2024. Available at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/nasas-voyager-1-resumes-sending-engineering-updates-to-earth
***