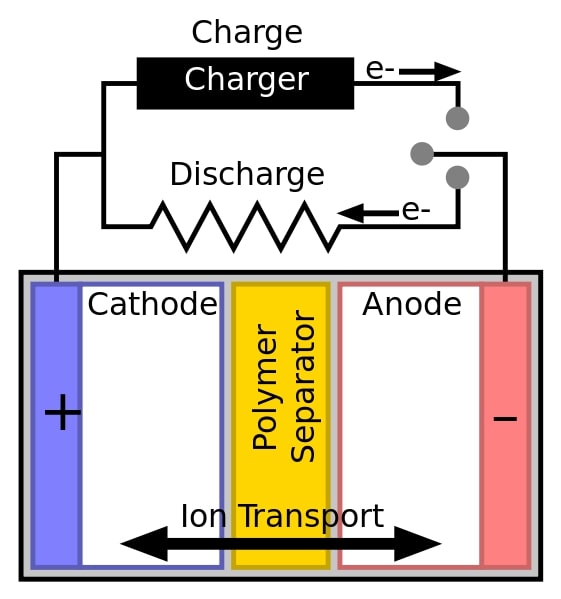
Lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles (EVs) face safety and stability issues due to overheating of separators, short circuits and reduced efficiency. With an aim to mitigate these shortcomings, researchers used a graft polymerization technique and developed innovative silica nanoparticles layered separators that are thermally stable and durable. Batteries with these separators are safer and showed improved performance. This development can contribute to adoption of EVs towards decarbonising transport sector.
The rechargeable Lithium-ion batteries (or Li-ion batteries or LIBs) have become exceedingly popular and ubiquitous in the last three decades. Due to high energy density, light weight and rechargeability, these are widely used in mobile phones, laptops, audio-visual devices, power storage and electric motor vehicles (EVs) and have become integral part of daily life. LIBs are eco-friendly, provide clean energy storage and contribute to decarbonising economy.
However, Lithium-ion batteries face safety risk for electric vehicles (EVs) and energy storage systems mainly due to overheating of polyolefin separators. The separators prevent direct contact between cathode and anode, but they melt when temperature increases to 160 °C due to overheating. As a result, anode and cathode may come in direct contact through formation of Li dendrites hence internal short circuits and inadequate absorption of electrolytes and reduced efficiency.
There have been efforts to deal with this shortcoming. Applying a coating of ceramics was thought of but found unsuitable because it increased thickness of the separators and reduced adhesion.
In a recent study, researchers Incheon National University used graft polymerization technique to attach a uniform layer of silicon dioxide (SiO2) nanoparticles to polypropylene (PP) separators. The separators thus modified with a coating of SiO2 of 200 nm thickness are more heat resistant and suppressed dendrite formation while maintaining energy storage capacity. This suggests that the polypropylene-based separator (PPS) of Li-ion batteries can be improvised to mitigate internal short circuits and to make the battery safer and efficient.
This development is pertinent and promising for LIBs in electric vehicles (EVs) and energy storage systems. Once commercialised, the improvised LIBs with better safety and efficiency can help uptake of eco-friendly electric vehicles.
***
References:
- Manthiram, A. A reflection on lithium-ion battery cathode chemistry. Nat Commun 11, 1550 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15355-0
- Park J., et al 2024. Ultra-thin SiO2 nanoparticle layered separators by a surface multi-functionalization strategy for Li-metal batteries: Highly enhanced Li-dendrite resistance and thermal properties. Energy Storage Materials. Volume 65, February 2024, 103135. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2023.103135
***